|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
The United States of America: A Failing Superpower
The United States of America (or the USA) borders with Canada, Mexico, Cuba (from Guantanamo Bay, Cuba) and is geographically half the size of Russia and slightly larger than Brazil or China. Size is a very big issue in the USA and Americans like having the biggest houses, the biggest cars and the biggest economy. But such things are no longer true. Americans have fallen on hard times and the future looks bleak for both jobs and the economy. The American economy has a number of factors that are weighing it down. Historically the US economy has been quite strong, and largely due to the US's political system which has a series of checks and balances in an effort to stem corruption, but corruption remains nevertheless. In 1776 the British colony of 13 states broke away from Great Britain and was recognized as the new nation of the United States of America following the Treaty of Paris in 1783. 37 more states followed as America adopted a philosophy of "Manifest Destiny", an idea that the United States should spread itself from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean.
THE WAR OF 1812During the War of 1812 (which lasted from 1812 to 1815) the USA even tried to expand their borders north through Canada, but were defeated by the combined forces of Canada and Great Britain. 2,260 American soldiers died during the conflict and enemy forces burned down the White House (revenge for the burning of the Canadian parliament in York, which is now modern day Toronto). British forces decided not to re-conquer the United States because they were too busy with Napoleon Bonaparte at the time so instead the USA and Britain signed the Treaty of Ghent in 1815. "The Star-Spangled Banner", America's National Anthem, was written in 1814 and is largely a tribute to the bombardment of Fort McHenry at Baltimore, Maryland, by the British Royal Navy. Sadly however many Americans do not know the proper words to the song, and even those who do only sing the first stanza of it (there are four stanzas total, but they are rarely ever sung because otherwise the song would take approx 10 minutes to sing).
THE CIVIL WARAmerica's history of violence doesn't end with the War of 1812 however, but they instead average a major war every 10 to 15 years. One of the largest is the American Civil War (1861 - 1865) during which the Union States in the North defeated the Confederate States in the South, who sought to separate and form their own nation. Key concerns with the American Civil War were: The abolition of slavery, voting rights for African Americans and various constitutional changes which gave the White House more power. In the years that followed there was a series of major dramatic changes in the USA: The assassination of President Lincoln, the Jim Crow laws which sought to segregate African Americans, industrialization of north-eastern states, the 1867 Alaska purchase from Russia, the Wounded Knee massacre in 1890, the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii in 1893, the Spanish-American War in 1898 (which resulted in the annexation of Puerto Rico and Guam) and a huge influx of European immigrants to America's coastal regions that lasted until 1929.
WORLD WAR IDuring World War I the United States stayed neutral and sold armaments to both sides of the conflict, aiming to get rich and didn't have the stomach to get involved with what was considered to be an European problem. Even when a German U-boat sank the British liner Lusitania in 1915, with 128 Americans aboard, U.S. President Woodrow Wilson vowed: "America was too proud to fight". Germany sought to convince Mexico to ally itself against the United States in the event the USA decided to enter the war in a telegraph intercepted by the British. The telegraph was later released to the White House and the American media, and when 7 American merchant ships carrying supplies to Britain were sunk by German submarines only then did the United States agree to fight back. By this point Germany and its allies were almost defeated. The United States entered the war at the proverbial last minute and a cease fire was eventually called on November 11th 1918. After the war was over the USA claimed the victory was their doing, but remained reluctant to be involved in European affairs. The USA did not ratify the Treaty of Versailles, which established the League of Nations in 1919 (which was later replaced by the United Nations in 1945). Thanks partly to their service during the war Native Americans gained American citizenship in the Indian Citizenship Act of 1924.
STOCK MARKET RISE AND CRASHA wave of industry after WWI resulted in a rise in debt as people sought bank loans and in turn invested in the stock market (a practice now considered foolish). This wave of personal debt and stock market investment looked great on paper until 1929 (Black Thursday, Black Monday, and Black Tuesday: October 24th, 28th and 29th) when the stock market crash and plunged many Americans into debt, unemployment and a financial collapse known at the Great Depression. Franklin D. Roosevelt (elected in 1932) responded a range of policies increasing government intervention in the economy. Prior to Roosevelt American's preferred a laissez-faire approach where politicians kept their hands out of economic matters, but due to the crash it became evident that the stock market needed rules and not allowing people to borrow cash to buy stocks was one rule that was quickly implemented. Drought during the 1930s also resulted in the Dust Bowl effect, wherein the lack of rain was so severe it caused much of central United States to turn to desert and dust storms wrecked havoc on impoverished agricultural communities.
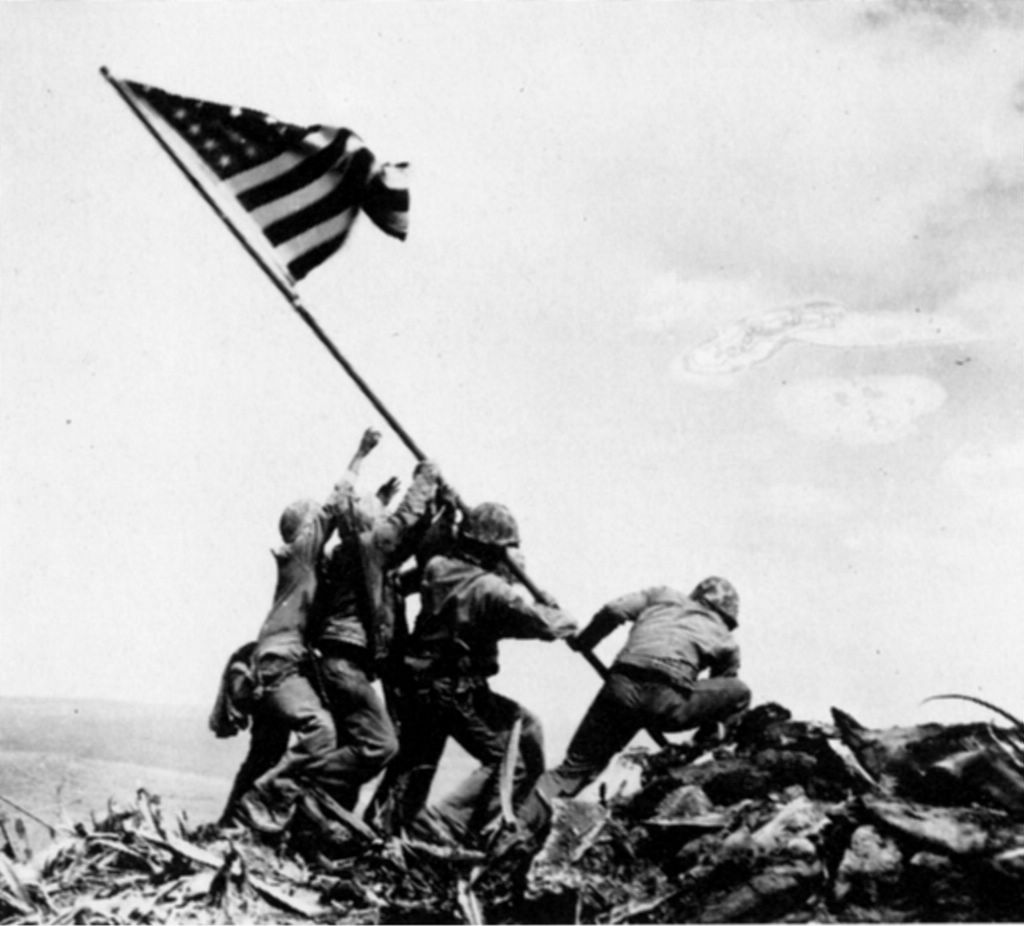
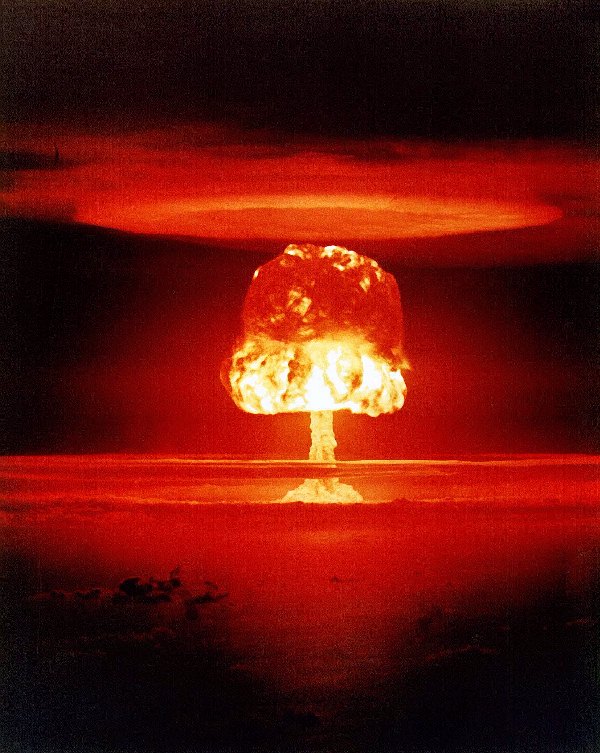
WORLD WAR IIBy 1936 the US had recovered from the Great Depression, but millions still lived in poverty. The outbreak of WWII in 1939 allowed for the US to start building armaments again and making a profit off of war, but again decided to stay neutral in the conflict. Only after the bombing of Pearl Harbour by the Japanese did the United States agree to enter the conflict on December 7th 1941. The war boosted the economy by providing capital investment and jobs, while bringing many women into the labour market. Despite being one of the most expensive wars in American history the United States actually managed to make a profit by turning their economy around and allowed the USA to double their lowest bracket income taxes. The United States also managed to cut short WWII by dropping two nuclear bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki in August 1945. Japan surrendered on September 2nd and ended the war. Japan's surrender saved Americans millions of dollars in what was becoming a very costly war, and was arguably impossible to win without nuclear weapons as the Japanese easily outnumbered Americans and had built up an unstoppable military. The use of nuclear weapons managed to save the United States from military and financial ruin.
THE COLD WAR & NASAAfter WWII it became clear that isolationism was not going to work and that it was not merely "European affairs" any more but a global environment. The USA helped to forge NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) and the Warsaw Pact, but also witnessed the rise and threat of Communism in Russia, China and around the world, resulting in the Cold War between NATO allies and Communist nations. Central to the Cold War was the difference in economic philsophies between Capitalism and Socialist Communism. Capitalism promotes private enterprise and laissez-faire government that doesn't interfere with how companies run their businesses. Socialist Communism promotes a centrally controlled economy and many state run institutions. In truth an economy needs both to be prosperous, but the question of where to draw the lines between the two is the issue at stake. In the United States schools, military, postal service, police, firefighters, road building and repair, parks, libraries and a plethora of other public services are controlled by the government, but with modern exception of health care which is privatized in the United States (the USA is the only country in the western world that doesn't have free health care). In a Communist nation like China for example electricity production, water distribution and many other public utilities are all run by the government. On a fundamental level the biggest difference is that Americans pay way more for electricity and water in the Unites States. In China water and electricity are so cheap its practically free, but China has other issues because the Chinese Communist Party is so authoritarian. Americans were so obsessed with this idea of free enterprise they tried to spread it overseas, and even fought in the in the Korean War from 1950–53 (America still has troops stationed in South Korea today) over the issue. When a ceasefire was called in 1953 the Korean peninsula was split into North Korea and South Korea, but the war never officially ended.
At the time there was also an anti-communist sentiment of "Better Dead than Red". The Senate House Un-American Activities Committee pursued a series of investigations into suspected leftist subversion, while Senator Joseph McCarthy became the figurehead of anti-communism who brough hysteria to new levels, trying to convince America that the Communists would attack the United States with nuclear weapons. The two economic philosophies were considered big issues back in the 1950s however and it was a virtual race between the United States and Soviet Russia to see who's idea was best. Nuclear weapons, the threat of nuclear war, the Arms Race and the Space Race is often viewed by modern psychologists and historians as historical examples of "dick waving" (trying to prove who has the bigger penis). The final battle between Capitalism and Communism never came however, although there was a close call in the form of the Cuban Missile Crisis in October 1962. An American U-2 spy plane revealed missile bases being built in Cuba on October 15th. The crisis ended two weeks later on October 28th when John F. Kennedy and United Nations Secretary-General U Thant reached an agreement with the Soviets to dismantle and remove the missiles in Cuba in exchange for a no invasion agreement and a removal of America's Jupiter and Thor missiles in Turkey. Long range intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) were not possible during this era and so dropping nuclear bombs thus was the territory of airplane bombers. Defending against those bombers NATO needed fighter planes that could reach Mach 1 or Mach 2 speeds in order to intercept bombers and shoot them down.
America was not the first country to develop supersonic jets however, that honour instead goes to America's northern ally Canada for developing CF-105 Avro Arrow which was the first jet plane and the first plane to break Mach 2. The CF-105 never went into production however and its production were mysterious shut down during a period of anti-Communist concern in Canada (worry Communists might try to sell the engineering plans to the Russians) and all their equipment destroyed or confiscated. Many of the Avro engineers later went to work for American companies and for NASA. In war the winner is usually the person who has the highest ground, so control of North American airspace would not be complete unless they could also defend against attacks from outer space as well. The RAAF recovery of a space craft in July 1947 in Roswell, New Mexico had many Americans worried that aliens or Communists had developed space weaponry and were paranoid about their national defense against such threats. In 1961 the Soviets launched the first manned spacecraft into outer space, which prompted President John F. Kennedy's call for the country to be first to land "a man on the moon," later achieved on July 20th 1969 by Buzz Aldrin and Neil Armstrong. Since then the United States has become a world leader in space exploration, launching numerous spy satellites, probes and developing the first space shuttle. The Russians meanwhile were content with smaller space modules and building the first space station Mir, which remained active from 1986 to 2001. Meanwhile back home in the United States many Americans were becoming restless under the Jim Crow laws which segregated and discriminated against African-Americans. Civil rights leader Martin Luther King, Jr. led the way to the abolition of such laws. Following John F. Kennedy's assassination in 1963, the Civil Rights Act of 1964 was passed under President Lyndon B. Johnson.
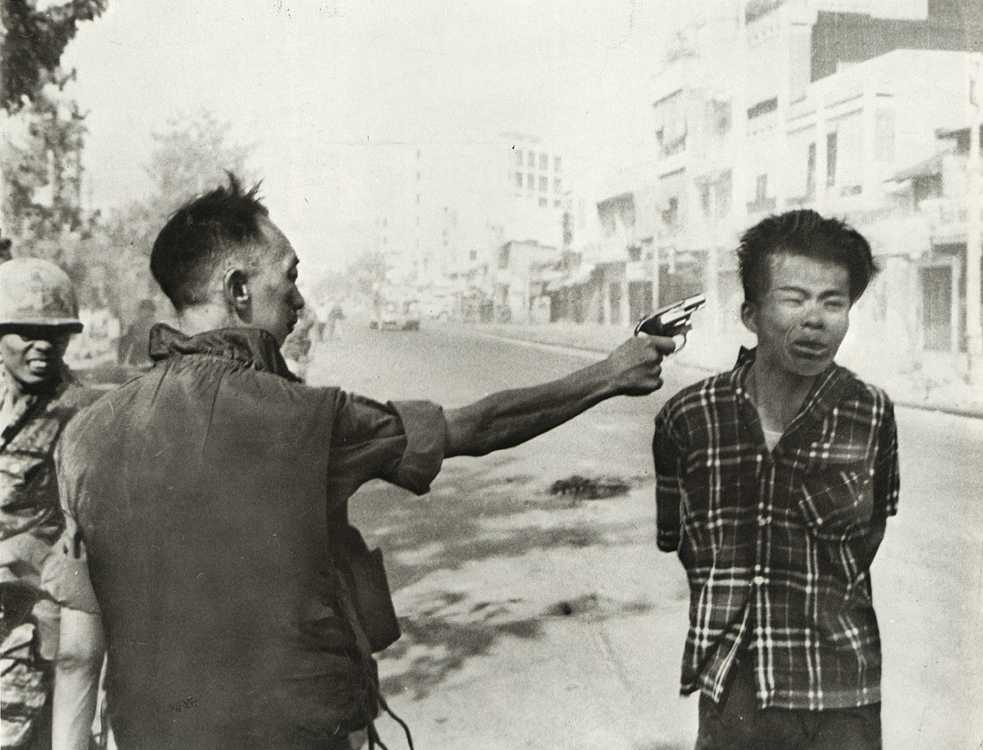
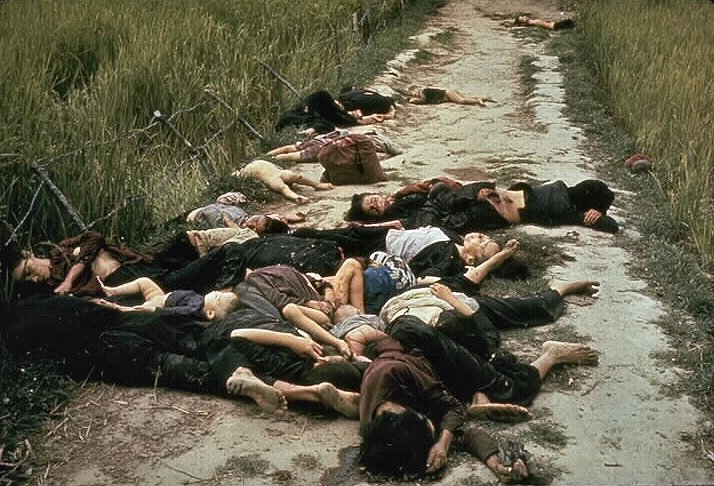
THE VIETNAM WARThe issue of civil rights didn't go away however. The Vietnam War from 1959 to 1975 was originally a proxy war through the US support of Ngo Dinh Diem who supported capitalism, who turned out to be an incompetent and greedy dictator and was later assassinated in 1963. Worried that South Vietnam might fall to Communism (and according to the Domino Theory, would spread to all of South East Asia) the United States had built numerous military bases in South Vietnam. Concerned about the safety of American troops in Vietnam however the war escalated and more troops were needed. On March 8th 1965, 3,500 United States Marines were dispatched to South Vietnam, which was increased to nearly 200,000 by December the same year. The war was not going well however as the military planners were not equiped to deal with guerilla tactics. Military losses were piling up and Americans began to question why they were in this war in the first place, especially since their South Vietnamese allies were corrupt and greedy murderers who were committing war crimes. In addition the Vietnam War draft had very large quotes and resulted in over 10,000 young American men skipping the country to Canada or Mexico to avoid the draft. Some also volunteered for domestic service, such as George W. Bush, who volunteered for the Texas Air Guard but spent most of his time AWOL. In October 1967 a large anti-war demonstration was held on the steps of the Pentagon. Of the thousands of protesters, over 680 were arrested. Some protesters chanted phrases like, “Ho, Ho, Ho Chi Minh! The NLF is going to win!” and "Hey, hey, LBJ! How many boys did you kill today?" During the 1968 election campaign Richard Nixon promised to help build up South Vietnam's military so they could support themselves more militarily and American troops could withdraw from the troubled region. The war was not going well and this shift was labelled the "Vietnamization" of Vietnam's military. Part of this strategy however meant widening the conflict in hopes of securing a war secure footing in the region. The My Lai Massacre on March 16th 1968 is an event where the US Army went on a killing rampage in the small towns of My Lai and My Khe, shooting and killing 504 Vietnamese civilians and children. Some of the victims were sexually abused, beaten, tortured, maimed and some of the dead bodies were mutilated. The media reports on the massacre sparked international and American condemnation of the war and permanently tarnished the reputation of "trigger happy" American forces in the region. After being elected Nixon visited China and tried to convince both China and Russia to stop helping the North Vietnamese military by supplying arms, in an effort to ease global tensions over the conflict, but both countries continued to supply arms to th Viet Cong. Nixon also tried to appeal to what he called the "silent majority" in the United States to support the war, blaming the silence of citizens during a period of mounting anti-war protests. Cambodia remained neutral during the conflict but was allowing Viet Cong forces to use Cambodian land along the Vietnam border as staging areas to launch attacks into Vietnam. In 1969 Nixon convinced Cambodian Prince Norodom Sihanouk that these launching areas would no longer be tolerated and the Cambodian government agreed to remove them or get drawn into the conflict. Prince Sihanouk was later removed from power in a 1970 coup by a pro-American supporter, but ultimately destabilized Cambodia and created more support for the Viet Cong. Starting in April 1969 the United States started dropping bombs along the Cambodian-Vietnam border, 2,750,000 tons of bombs in total over a 14 month period (more than the total dropped by the Allies during World War II). The bombing was hidden from the American public.
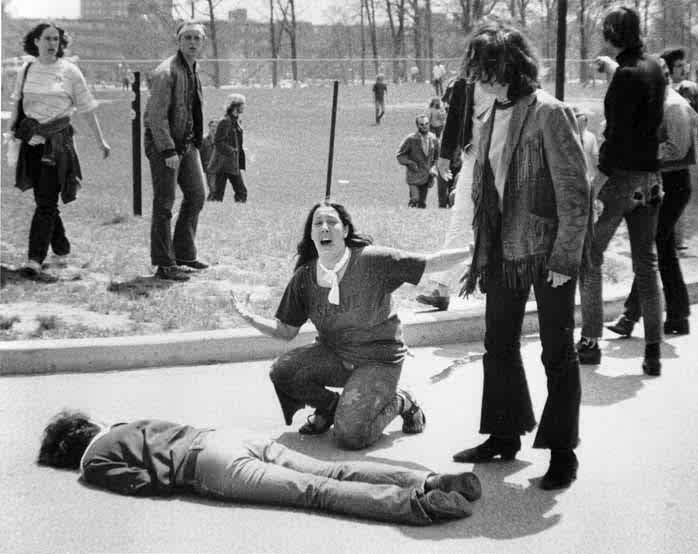
Following the coup of Prince Sihanouk in 1970 Cambodia's borders became closed and the United States invaded Cambodia, claiming they were trying to buy time for the South Vietnamese army to gain advantage against the Viet Cong. Nixon announced the invasion of Cambodia on April 30th 1970 on national television. The invasion of Cambodia however sparked protests back in the United States, most notably at Kent State University in Ohio. The Ohio National Guard was called in to remove the protestors and shot into crowds of people, killing four students, some of them bystanders. In response to the shootings hundreds of universities, colleges, and high schools closed throughout the United States due to a student strike of eight million students, and the event further divided the United States public over the war. In 1971 the Pentagon Papers were leaked to The New York Times. The top-secret history of U.S. involvement in Vietnam, commissioned by the Department of Defense, detailed a long series of public deceptions. The same year the South Vietnamese army launched an attack in neighbouring Laos, a neutral country. Despite the American training and Vietnamization of the South Vietnam military the action was a complete rout. They met with unforeseen resistance and went into full scale retreat. When they ran out of fuel, soldiers abandoned their vehicles and attempted to barge their way on to American helicopters sent to evacuate the wounded. Half of the invading South Vietnamese troops were either captured or killed. The operation was a fiasco and represented a clear failure of Vietnamization, despite many of their military leaders being shipped back and forth to the United States for training over a period of 10 to 15 years.
In 1971 Australia and New Zealand withdrew their soldiers. The U.S. troop count was further reduced to 196,700, with a deadline to remove another 45,000 troops by February 1972. In 1972 Henry Kissinger, Nixon's National Security Adviser, continued secret negotiations with North Vietnam's Le Duc Tho. In October 1972, they reached an agreement, but South Vietnamese President Thieu demanded massive changes to the peace accord. When North Vietnam went public with the agreement's details, the Nixon administration claimed that the North was attempting to embarrass the President and the negotiations became deadlocked. Hanoi demanded new changes and to force Hanoi back to the negotiating table, Nixon ordered Operation Linebacker II, a massive bombing of Hanoi and Haiphong's civilian factories from December 18th to 29th. The bombing destroyed much of the remaining economic and industrial capacity of North Vietnam. Popularly known as the Christmas Bombings, the civilian death toll (1624 civilians killed) provoked a fresh wave of anti-war demonstrations back in the United States. On January 15th 1973, Nixon announced the suspension of offensive action against North Vietnam. The Paris Peace Accords on "Ending the War and Restoring Peace in Vietnam" were signed on January 27th 1973, officially ending direct U.S. involvement in the Vietnam War. American troops pulled out in stages between 1973 and 1975.
THE WATERGATE SCANDALOn June 17th 1972 five men being arrested after breaking and entering into the Democratic National Committee headquarters at the Watergate hotel complex in Washington, D.C. Investigations conducted initially by the FBI, and then later by the Senate Watergate Committee, House Judiciary Committee and the press revealed that this burglary was just one of many illegal activities authorized and carried out by Nixon's staff and those loyal to him. They also revealed the immense scope of crimes and abuses, which included campaign fraud, political espionage and sabotage, illegal break-ins, improper tax audits, illegal wiretapping on a massive scale, and a secret slush fund laundered in Mexico to pay those who conducted these operations. President Nixon and his staff conspired to cover up the break-in. After enduring two years of mounting evidence against the President and his staff, which included former staff members testifying against Nixon in a Senate investigation, it was revealed that Nixon had a tape recording system in his offices and that he had recorded many conversations. Recordings from these tapes (later called the Smoking Gun evidence) revealed that he had obstructed justice and attempted to cover up the break-in. After a series of court battles, the United States Supreme Court unanimously ruled in United States v. Nixon that the President had to hand over the tapes and he eventually complied. With certainty of an impeachment in the House of Representatives and of a conviction in the Senate, Nixon resigned ten days later, becoming the only U.S. President to have resigned from office. His successor, Gerald Ford, would issue a controversial pardon for any federal crimes Nixon may have committed while in office.
THE ENERGY CRISISDuring the 1970s the United States was hit by two separate oil shortages, sparking concerns of an energy crisis. The 1973 oil crisis began on October 17th 1973, when the members of Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC, a subgroup of OPEC) announced that they would no longer ship oil to nations that had supported Israel in the Yom Kippur War with Syria, Egypt, and Iraq (the United States, NATO allies and Japan). OPEC members agreed to use their leverage to deliberate raise world oil prices. Because of the dependence of the industrialized world on crude oil and the predominant role of OPEC as a global supplier, these price increases were dramatically inflationary to the economies of the targeted countries, while at the same time suppressive of economic activity. The targeted countries responded by creating fuel efficiency standards for automobiles in order to cut dependency. The 1979 oil crisis in the United States occurred in the wake of the Iranian Revolution. Amid massive protests, the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, fled his country in early 1979, allowing Ayatollah Khomeini to gain control. The protests shattered the Iranian oil sector. While the new regime resumed oil exports, it was inconsistent and at a lower volume, forcing prices to go up. Saudi Arabia and other OPEC nations, under the presidency of Dr. Mana Alotaiba increased production to offset the decline, and the overall loss in production was about 4 percent. However, a widespread panic resulted, driving the price far higher than would be expected under normal circumstances. During the 1980 Iraqi invasion of Iran oil production in Iran nearly stopped, and Iraq's oil production was severely cut as well. Oil prices began a six-year decline that culminated with a 46 percent price drop in 1986. This was due to reduced demand and over-production, and caused OPEC to lose its unity. Oil exporters such as Mexico, Nigeria, and Venezuela expanded. The US and Europe got more oil from Prudhoe Bay and the North Sea. The energy crisis would rear its head again in 1990, but was milder and more brief than the previous two. It lasted only six months and occurred as a result of the first Gulf War. As Saddam Hussein's forces in Kuwait retreated they set the oil fields of Kuwait on fire. The OAPEC decided that since the oil production in the Kuwait was falling, they would increase their oil supply and stabilize the oil market. Oil hit a then-record of $50.50 per barrel during the 1990 crisis.
AMERICAN ACTIVITIES IN THE MIDDLE EASTThe dependency on oil fueled several wars during the 1980s and helped to cut oil prices during that period. The United States was not the only country with designs on the region and Russia had a vested interest in obtaining the black gold of the oil rich Middle East. Soviet Occupation of Afghanistan Soviet forces first sent troops into Afghanistan on August 7th 1978 but the official invasion didn't begin until December 7th 1979, with a much larger scale invasion onn Christmas Eve 1979 when over 100,000 Soviet troops entered Afghanistan. They knocked out Afghanistan's military communication centre in the city of Kabul and executed Afghanistan's President Hafizullah Amin. Afghanistan's military was scattered, leaderless and fell easily before Soviet tanks and airpower. Afghanistan's religious freedom fighters (the Mujahideen) was forced into guerrilla warfare. Soviet troops were centralized in cities amongst civilian populations that could be easily controlled and bullied, but Afghanistan's military went underground (literally in some locations where caves provided excellent shelter from Russian assaults). During the initial invasion the Soviet troops were supported by 100,000 members of Afghanistan's Parcham faction (a socialist group with communist leanings) in hopes of creating a socialist-communist state. Precise numbers of the death count are unknown, but range between 600,000 to 2 million. Another 5 million Afghans fled the country during the initial conflict. As part of its Cold War strategy the United States under the leadership of Jimmy Carter began training the Mujahideen in an effort to undermine Soviet oil interests in the Middle East. The Mujahideen fought back against the communist regime and it wasn't until 1989 when the Soviet Union collapsed did Soviet troops finally withdraw from Afghanistan. The withdrawal was seen as an ideological win for the United States which was trying to keep Middle East oil out of communist hands. The CIA provided assistance to the Mujahideen freedom fighters through the Pakistani secret services, Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), in a program called Operation Cyclone. Approx. $20 billion in U.S. funds were funneled into Afghanistan to train and equip troops with weapons, including Stinger surface-to-air missiles. After the communists left, so did the Americans, leaving the Afghanistan people to rebuild their wartorn country.
After Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini took control of Iran, creating a conservative Shi'ite Islamic state the repercussions in Iraq were felt by Saddam Hussein, who believed in religious moderation and the separation of church and state. In 1980 Hussein claimed that Iranian forces was attempting to overthrow his government and declared war on Iran. The Iranian army was disbanded after the Iranian Revolution and was ill-equipped during the start of the war. Saddam Hussein's primary target was the region of Khuzestan which not only has a substantial Arab population, but boasted rich oil fields as well. By 1982 Iran managed to force Iraqi forces back across the Iraq border. It could have ended there but the United States provided Iraqi forces with chemical/biological weapons and guns which they used to attack Iranian soldiers and civilians. Meanwhile the United States sold chemical weapons to Iran, playing both sides for fools in exchange for cheap oil from both countries. Iran was also sold chemical weapons from China, but no where in the amount that Iraq received from the United States. According to CIA reports the United States sold Iraq enough chemical and biological weapons (including sarin gas) to kill the entire human population of Earth four times over. Thankfully sarin gas and many other chemical agents degrade over time and becomes useless after several years. The United States also gave Saddam Hussein intelligence reports from US spy satellites to help him plan attacks on Iran and the US Air Force shot down an Iranian airliner. The war dragged on until 1988 until Khomeini and Hussein accepted a truce brokered by the United Nations.
In 1990 Saddam Hussein found out that the country of Kuwait was stealing Iraqi oil and selling it the United States and other western countries. Iraq invaded Kuwait and Saddam Hussein declared Kuwait was now part of Iraq, an act which enraged the United States and cut them off from a cheap oil supply. The United Nations passed sanctions against Iraq and demanded the withdrawal of Iraqi troops from Kuwait. With heavy pressure from the United States the UN Security Council voted for military action against Iraq, authorizing "all necessary means" to "restore international peace and security in the area." The United States and coalition forces entered the war with more advanced weaponry than that of Iraq and quickly defeated the Iraqi army in a mere seven months. Iraq's army was one of the largest and best armed forces in the Middle East at the time, but they were sorely outmatched and outnumbered for what was largely an air war over Kuwait. In the end Saddam Hussein removed his troops from Kuwait, but not before setting fire to all the oil wells as retribution for Kuwait's thievery. During the war there was heightened concern that Saddam Hussein might use chemical weapons against American and allied troops. Soldiers were given equipment to combat chemical weapons and anthrax vaccine in the event the Iraqis used biological weapons, but these fears were unfounded as Iraq had very little chemical/biological weapons left over from the previous war. What Iraq did have however was Al-Hussein missiles, which is a Soviet-era Scud tactical ballistic missile which they used against both Saudi Arabia and Israel (the USA has military bases in both countries) and in theory could be used to deliver chemical, biological or nuclear weapons, but Iraq used them for explosives only. At the end of the war coalition forces decided to go home and then US president George H. W. Bush had a choice to make: Overthrow Iraq and try to occupy the country, or go back home? Bush chose the latter because of the economic consequences of trying to continue a war that the American public had no interest in paying for. In return for peace Iraq agreed to accept "no-fly zones," dismantle all chemical and biological weapons it possessed, and end any attempt to create or purchase nuclear weapons. UN weapons inspectors would evaluate the dismantlement of such weapons and Iraq would face economic sanctions if they disobeyed.
INVASION OF PANAMACodenamed Operation Just Cause, the invasion of Panama deposed Panamanian dictator Manuel Noriega in December 1989, during the presidency of George H. W. Bush. From 1959 to the early 1980s Manuel Noriega served as a U.S. intelligence asset and was on the Central Intelligence Agency's payroll. Noriega's relations with George H. W. Bush began in the 1970s, when Bush was head of the CIA. The CIA paid Noriega $100,000 US for sabotaging the communist Sandinistas in Nicaragua and the revolutionaries in El Salvador. Noriega also helped the Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) to restrict illegal drug shipments from South and Central America, while simultaneously working with the drug cartels and taking bribes from both sides (he was later indicted for multiple drug-related offenses). In return for Noriega's help the CIA helped him to take over Panama in August 1983. Noriega enhanced his position as de facto ruler in August 1983 by promoting himself to full general. Noriega, being paid by the CIA, extended new rights to the United States and allowed the U.S. to set up listening posts in Panama. He aided the American-backed guerrillas in El Salvador and Nicaragua by acting as a conduit for U.S. money and weapons. The CIA saw Noriega as a double agent (his nickname was "rent-a-colonel") and believed that he was also selling information to communist Cuba.
In 1989 Noriega lost an election to Guillermo Endara, but nullified the election results due to "foreign interference" and publicly brutalied his political opponent Endara, who had rightfully won the election. In October 1989 Noriega foiled a military coup attempt. Pressure mounted on George H. W. Bush as the mass media labeled him a "wimp". Bush announced the invasion of Panama on December 20th, during which he cited protecting American citizens in Panama, democracy, human rights, illegal drug trafficking and several treaties obligating the United States to invade. The Panamanian people overwhelmingly supported the action. According to one poll 92% of Panamanian adults supported the incursion by the USA, and 76% wished that U.S. forces had invaded sooner in October. Dissenters list a civilian death of toll between 3,000 and 15,000 as a major grievance against the war. The war lasted a mere 43 days, from December 20th 1989 to January 31st 1990, but afterwards there was a period of widespread looting and lawlessness, a contingency which the United States military had not anticipated and it took years for Panama's economy to recover. On July 19, 1990, a group of 60 companies based in Panama filed a lawsuit against the United States Government in Federal District Court in New York City alleging that the U.S. action against Panama was careless and negligent of civilian life and property. THE RISE OF TERRORISM
In 1992 President Bill Clinton took office in the White House and ushered in an era of economic prosperity in the United States, the longest and the largest economic expansion in modern U.S. history. It was also a period that saw Islamic Terrorism rise against American control of the Middle Eastern oil. Terrorists attacked the World Trade Center and attacked U.S. forces in Somalia in 1993, bombed the Khobar Towers in 1996, bombed United States embassies (Tanzania and Kenya) in 1998 and the USS Cole bombing in Yemen in October 2000. These attacks were primarily motivated by American interference in Middle Eastern politics such as the Soviet Occupation of Afghanistan, the Iran-Iraq War and the Gulf War. Those wars radicalized the region and create Islamic extremism in the Middle East and strong anti-American sentiment. There was also domestic terrorism such as the Waco Massacre on February 28th, 1993 when the United States Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, and Firearms (ATF) attempted to execute a search warrant at the Branch Davidian ranch at Mount Carmel, a property northeast of Waco, Texas. An exchange of gunfire resulted in the deaths of four federal agents and six Davidians. A subsequent 51-day siege by the FBI ended on April 19th when fire destroyed the compound. Seventy-six people, including 21 children and two pregnant women, along with Davidian leader Vernon Wayne Howell, better known as David Koresh, died during the fire.
Another domestic terrorism incident happened on April 19th, 1995, the bombing of the Alfred P. Murrah Federal Building, an office complex in downtown Oklahoma City. The attack was planned by Timothy McVeigh and Terry Nichols in retaliation for the Waco incident (the bombing occurred on the anniversary of Waco). The attack killed 168 Americans and injured over 800. A third incident was not directed at the government but at American students. The Columbine High School massacre occurred on April 20th, 1999 in Jefferson County, Colorado, near Denver and Littleton. Students Eric Harris and Dylan Klebold went on a shooting rampage, killing 12 students and a teacher and injuring 23 others before committing suicide. It was the fourth-deadliest school killing in United States history, after the 1927 Bath School disaster, the 2007 Virginia Tech massacre and the 1966 University of Texas massacre. Lack of gun control laws, youth gun violence, bullying, violent movies and video games, Marilyn Manson music, lack of school security, goth culture, anti-depressants were a list of things blamed for the incident.
THE KOSOVO WARBetween 1991 and 2001 the region of Yugoslavia became embroiled in a series of ethnically divided wars between Serbs, Croats, Bosnians and Albanians. The first was the War in Slovenia (1991), followed by the Croatian War of Independence (1991-1995), the Bosnian War (1992-1995), NATO bombing of Republika Srpska (1995-96), the Kosovo War (1996-1999), NATO bombing of Yugoslavia (1999), the Southern Serbia conflict (2000-2001) and the Macedonia conflict (2001). The United States became involved in these wars, trying to broker peace in the difficult region, but was extremely reluctant to commit American forces for a ground offensive. NATO deemed the region important to European stability, but on the homefront most Americans couldn't even find Yugoslavia on an unmarked map. Public interest in the wars going on in the Balkans was little and Americans were far more interested in Bill Clinton's sexual affairs with Monica Lewinsky, Paula Jones, Kathleen Willey and others. To stop ethnic cleansing and genocide of Albanians by nationalistic Serbians Bill Clinton authorized the use of American troops in a NATO bombing campaign against Yugoslavia in 1999, named Operation Allied Force. General Wesley Clark was Supreme Allied Commander of NATO and oversaw the mission and the bombing campaign later ended on June 10th, 1999. An United Nations resolution placed Kosovo under UN administration and authorized a peacekeeping force. NATO claimed to have suffered zero combat deaths and two deaths from an Apache helicopter crash. Despite opposition to American involvement which criticized pre-war genocide claims an U.N. Court ruled that "a systematic campaign of terror, including murders, rapes, arsons and severe maltreatments" aimed at "ethnically cleansing the region" did take place. Yugoslavian President Slobodan Miloševic was eventually charged with the "murders of about 600 individually identified ethnic Albanians" and "crimes against humanity." While problems in the former Yugoslavia were intense it was not the Kosovo War that distracted the United States from the Monica Lewinsky scandal. To weaken Saddam Hussein's grip over Iraq, Bill Clinton signed a law on October 31st 1998, which instituted a policy of "regime change" against Saddam Hussein. The Clinton administration then launched a four-day bombing campaign named Operation Desert Fox from December 16th to December 19th, 1998 in an effort to destroy any remaining weapon plants Iraq might still have and destabilize Hussein's power.
SEPTEMBER 11TH, 2001On September 11th 2001 (often referred to as 9/11) a series of coordinated suicide attacks by the terrorist group al-Qaeda struck the World Trade Centre in New York and the Pentagon located in Arlington, Virginia. 19 al-Qaeda terrorists hijacked four commercial passenger jet airplanes and intentionally crashed two of the airliners into the Twin Towers of the World Trade Center in New York City, killing everyone on board and many others working in the building. Both buildings later collapsed within two hours, destroying at two other nearby buildings and damaging others. The hijackers crashed a third airliner into the Pentagon and a fourth plane was shot down by the American Air Force and crashed into a field near Shanksville in rural Somerset County, Pennsylvania. 2,974 people died in the terorist attacks, 6,291 people were injured and another 24 were never found and presumed dead. Stock exchanges closed for almost a week, and posted enormous losses upon reopening, especially in the airline and insurance industries. The economy of Lower Manhattan ground to a halt, as billions of dollars in office space was damaged or destroyed. The attacks are believed to have been organized by former CIA-agent turned terrorist leader Osama bin Laden. Bin Laden was a spy for the CIA during the Gulf War, but after Iraq surrendered in 1992 he developed a deep hatred of the United States and their oil ambitions in the Middle East. A relative of the Saudi Arabian royal family, Osama bin Laden recruited 15 terrorists from Saudi Arabia, one from Egypt, two from the United Arab Emirates, and one from Lebanon. The number of terrorists from Saudi Arabia has sparked debate whether the United States should be more worried about Saudi Arabian terrorism and not Afghanistan or Iraq.
The sudden straight downwards collapse of the World Trade Centre has sparked debate amonst demolition experts as to whether the buildings were deliberately collapsed. According to the "9/11 Truth Movement" the buildings should not have collapsed at all as heat alone from jet fuel is not sufficient to melt steel girders, but instead controlled blasts in video footage can be seen directing the collapse of the structure downwards. Larry Silverstein, the leaseholder and insurance policy holder for the remainder of the World Trade Centre Complex, reportedly needed to collapse/deconstruct the buildings due to asbestos, but the process would be costly and damage nearby buildings. Instead he conveniently took out a huge insurance policy months prior to September 11th, sparking conspiracy theories that he and the White House had prior knowledge of al-Qaeda threats against the building. George W. Bush's call for relaxing airport security in January 2001 suggests the White House also knew (or planned according to conspiracy theorists) of threats against the World Trade Centre and instead of bolstering security actively worked to allow the events to take place.
THE WAR ON TERRORISMFollowing the events of September 11th the Wolfowitz Doctrine became a central aspect of US foreign policy. The document was leaked to The New York Times on March 7th, 1992 and outlines a policy of unilateralism and pre-emptive military action to suppress potential threats from other nations and prevent any other nation from rising to superpower status. This policy was then applied to "Axis of Evil" nations that according to the Bush Administration posed a security threat to the United States. President George W. Bush in his State of the Union Address on January 29th 2002 referred to an "Axis of Evil" comprised of the countries Iraq, Iran and North Korea. Since then the United States has looked for ways to impose regime change on those countries and look for excuses to go to war and lay in pre-emptive strikes against "Axis of Evil" countries. This was a dramatic turning point for United States foreign policy. The war against terrorism could be used to bully both allies and enemies, and if necessary be used to work unilaterally without United Nations or NATO permission or help. The American public's obsession with revenge caused them to ignore things like their basic freedoms being stripped away by things like the Patriot Act, which allowed the US government to invade the privacy of civilian Americans and conduct activities previously considered illegal such as wiretapping, torture and imprisonment without trial. The Bush Administration also created a new department: Homeland Security, which has frequently been criticized for using German gestapo tactics and ignoring basic human rights. The Department of Homeland Security also created a national threat advisory, which has been criticized for being useless and only serving to scare the general populace. During George W. Bush's 2004 re-election campaign he ran on a platform of fear, using America's fear of more terrorist attacks and worry about Weapons of Mass Destruction to get himself elected. In 2000 Bush's rise to the Oval Office has been widely criticized by political pundits as being an election sham due to what appeared to be rigged voting machines and bad ballots in Florida where George Bush's brother Jeb Bush was governor at the time. Thanks to his new election platform Bush managed to coast into a second term with little rumour of it being a rigged election. Other countries have joined the Bush Administration's war on terror, but the degree of success is limited to Britain, Canada, Australia, Japan and various allies. Some allies have withdrawn their military support for the war after being targeted by terrorism, such as the 2004 Madrid train bombings which swayed public opinion in Spain and they withdrew military support. Britain which was struck by subway and bus bombings during rush hour on July 7th 2005 (known as 7/7) which killed 56 people and injured approx. 700, but the British government was unfazed by the incident. The British had previously built up some backbone during the Irish Republican Army's bombings during the 1980s and 1990s (the Pan Am 103 bombing killed 270 people in 1988). Terrorist groups affiliated with al-Qaeda has been targeting countries and organizations that support the United States and/or America's oil ventures in the Middle East. Countries such as Libya, Syria, Jordan and Palestine have also been on Homeland Security's watch list, but very little attention has been paid to African countries where war has broken out in recent years and are potential recruiting grounds for terrorist groups.
Afghanistan 27 days after the September 11th attacks the United States invaded Afghanistan on October 7th 2001. Despite an easy victory in the airspace over Afghanistan and securing key northern cities, Afghanistan is still very much a divided country. The deposed Taliban government still operates in the southern regions, collects taxes and provides safety and protection while harvesting opium crops to help pay for munitions to fight back. The war in Afghanistan has been hampered by a shortage of American and allied troops. The Bush Administration relocated many of the troops in March 2003 to fight in Iraq, leaving Afghanistan bitterly divided and sorely undermanned. Troops and civil engineers have been working to build roads and an oil pipeline that will run across the width of Afghanistan to the Chinese border in the north east. Like the Soviets in the 1980s the Americans/allied troops are encountering difficult resistance from the Mujahideen, Taliban and al-Qaeda fighters in the region. Roadside bombs and similar attacks kill American and allied troops on an almost daily basis. The United States and allies hope the war in Afghanistan can be won through a combination of education, economic changes and what has essentially has boiled down to a public accountability war. Corruption within the new Afghan government and regular friendly fire incidents that kill Afghan civilians are hampering American efforts, making the United States look like "trigger happy" fanatics and no better than the fanatics they're trying to defeat.
Iraq The invasion of Iraq on March 20th 2003 went off without a hitch. Saddam Hussein was eventually captured on December 14th 2003, tried for war crimes from 2004 to 2006 and abruptly hanged without US approval on December 30th 2006. No weapons of mass destruction, the key political reason for the pre-emptive war on Iraq was ever found. The oil-for-food program, first created by the Clinton administration, has been instrumental in getting the United States cheap oil while construction of new oil pipelines are underway. Like Afghanistan the United States hopes to win through a combination of education, economic changes, but again political/police corruption and friendly fire incidents are hampering American efforts. Under Saddam Hussein religious and sectarian problems were violently stamped out and the population lived in a state of fear. Under American rule religious groups have grown militant and started attacking each other. Fighting between different Iraqi religious factions (Sunni and Shia Muslims) has destabilized the country to the point that American troops are now stuck in the middle of a religious civil war.
Iran Iran's military ambitions and nuclear program has the White House nervous about attacking the country. Iran has not yet tested nuclear weapons, but has not ruled out the possibility of testing them in the future. Iran maintains that it has the right to nuclear power for electricity reasons, and is considering pursuing nuclear weapons as a defensive precaution. A fundamentalist Muslim country with the potential for nuclear weapons has many God-fearing Americans worrried, but it is not the only reason for a possible war with Iran. The United States is helping to build an oil pipeline from Iraq, through Iran and Afghanistan to the Chinese border and the Iranian government is the last remaining obstacle to that oil pipeline. Iran's military strength is overwhelming with 900,000 active troops and a civilian militia of 11 million men and women. Iranian women make up a surprisingly large chunk of the militia and any war with Iran would require substantial human resources and likely result in a draft. Mahmoud Ahmadinejad, Iran's president, is a devout anti-semite and appears bent on nuclear war with Israel (which also possesses nuclear weapons) and frequently rattles his sabre to that effect. Political tensions between the United States and Iran run high and oil prices skyrocket whenever threats of war are made. China has been trading Iran ballistic missile technology since the 1980s in exchange for oil.
North Korea North Korea test detonated a nuclear weapon on December 9th, 2006. Since 1950 the United States and North Korea have officially been at war, but have agreed to a ceasefire since 1953. Peace between the two nations and South Korea was never officially recognized and North Korea still intends to someday invade and conquer South Korea. The United States has approx. 30,000 troops currently stationed in South Korea, always prepared for an invasion from North Korea and running nuclear attack simulations. Because North Korea has no vital resources such as oil however the United States has been surprisingly mum on the issue. North Korea wants economic aid for its failing "hermit" economy which has fallen apart since the collapsed of Communism in Russia (once a key trading partner) and China's rapidly increasing capitalism. North Korea's leader, Kim Jong Il, is considered in military circles to be a buffoon and isn't taken too seriously. He's more interested in Hollywood movies and styles himself a patron of the arts rather than a corrupt dictator (which he still is). He onced had North Korean troops kidnap a favourite South Korean actress just so she could perform for him. North Korea has also been testing intercontinental ballistic missiles, but thus far has been unsuccessful in building one able to reach the United States. A North Korean submarine would be needed to deliver the missile to an appropriate range.
A Modern Look at the Economy of the United StatesThere are a combination of factors that are hurting the economy of the United States, creating a dire outlook for the future.
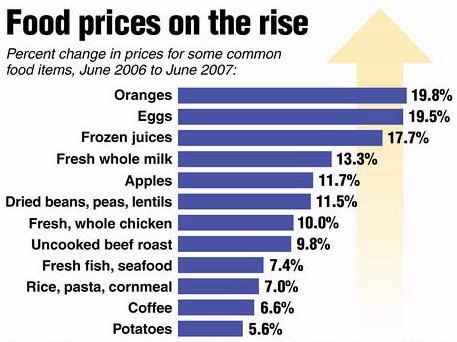
AGRICULTURE & FOOD PRICESPart of the reason why the United States' economy has historically been so robust is because of the agricultural subsidies that help out American farmers and keep food prices relatively low. Food in the USA is relatively cheap and plentiful compared to much of the world's population, and cheap food means people don't have to worry about feeding themselves as much and can spend their money elsewhere, thus helping the US economy. The recent doubling in oil/gas prices has resulted in farmers spending more money on fuel to plant and harvest their crops. The biofuel industry has not been helping either as it has resulted in skyrocketing corn prices (corn starch and other byproducts are used in a lot of foods) and then there is the matter of droughts and rain shortages due to global warming and climate change. The loss of potential crops is causing food prices to go up. Agriculture is also responsible for the growth of cotton, leather and other products used in the fashion industry. Thus the same problems also effects the prices of clothing in the USA. The American textile industry is now facing huge competition from Asian competitors who can produce large quantities of quality clothes for significantly less. Many companies like Walmart, Levis, Nike and the GAP are moving their operations overseas, thus hurting the American textile industry. Lastly, gas prices also effects the transportation of food/clothing, thus creating a double whammy effect on consumer prices. The rise in food/clothing prices has resulted in inflation in the United States going to its highest level in 17 years (2008).
ASIAN COMPETITION/IMPORTSAsian competition and imports to the United States effect many industries and companies, but one of the most notable is American automotive manufacturers Ford, General Motors and Chrysler have all announced major cutbacks in the last several years. GM announced in 2008 it needs to cut $15.5 billion from its annual budget or declare bankruptcy. These job losses are dragging down the US economy as it takes well paid factory jobs out of America and sees the workload shifted to less expensive Asian manufacturers. The automotive industry recession is only one of a growing problem. Overall America's manufacturing sector is being hurt by Asian imports and major corporations like General Electric are being forced to move some of their operations overseas just to remain competitive and maintain their stock prices. General Electric for example has lost over half of its stock value since 2001, from a combination of fiscal mismanagement and Asian competition. Manufacturing and construction sectors have seen huge job losses in 2007 and 2008. America lost 383,000 manufacturing jobs between August 2007 and July 2008 and another 557,000 construction jobs during the same period due to the subprime credit crisis and fall of housing prices. The combined collapse of both housing and manufacturing industries is creating a domino effect which is effecting consumer spending in other industries. There is a solution to curbing Asian imports, but it means raising tariffs on Asian imports dramatically and withdrawing from various trade agreements. Some economists think this would hurt the US mining and lumber industries, but to paraphrase Canadian Prime Minister Jean Chretien "What do we sell them that they don't need?" The Asian economy needs minerals and lumber for its manufacturing/construction sectors, which means even if the United States raised tariffs the Asians would still keep buying our minerals and wood. As it currently stands the US has a trade imbalance with China and other Asian countries. In 2007 alone China exported $321.4 billion US worth of goods to the United States and received in return only $65.2 billion US worth of goods, resulting in a trade imbalance of $256.2 billion US. In 2008 that trade imbalance is expected to break $290 billion as China floods the USA with cheap consumer goods. (Source: U.S. Census Bureau, Foreign Trade Division.)
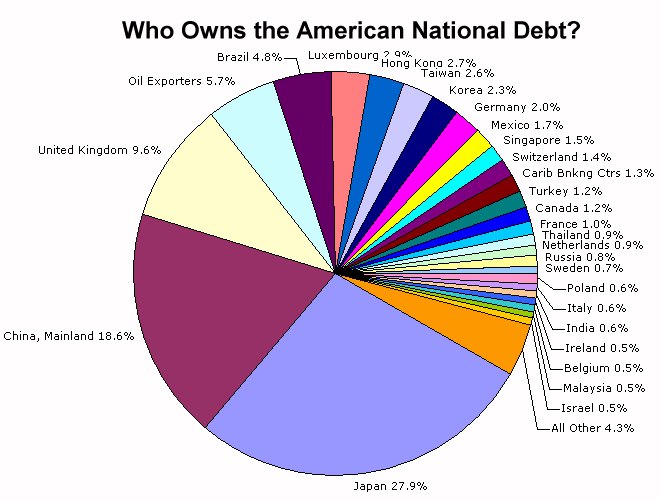
BUDGET DEFICITAccording to the Bush Administration there will be a record federal budget deficit in 2008 that approaches $490 billion US. The deficit is being driven to record levels by the sagging economy and the economic stimulus payments being made to 130 million households in an effort to keep the United States from falling into a deep recession. $490 billion would easily surpass the record deficit of $413 billion set in 2004 during the height of the war in Iraq. The number represents approx. 3% of the size of the economy, which is the deficit measure seen as most relevant by economists. It is a significantly larger % compared to other deficits of the 1980s and early 1990s, when earlier Reagan and Bush Sr. administrations cobbled together politically painful taxes aimed at reducing the deficit. The budget deficit is important because that money has to be borrowed from large global banks and corporations, notably Chinese and Japanese banks which own 46.5% of America's $9.7 trillion National Debt (as of Sept. 2008). The USA then pays a high interest rate on the National Debt, which has to be paid off eventually with taxes. Depending on the type of taxes and how it effects America's working class tax increases could significantly lag the American economy. Debate about taxing the working class has fueled ideas about whether the USA should introduce a luxury tax on gold, silver, expensive cars, electronics and other consumer goods bought primarily by the rich and well off. Evidently the White House needs to make tough choices about reducing the National Debt. Under the Clinton Administration the White House raised income taxes on the rich and upper class and between 1998 and 2000 paid off $355 billion US of National Debt and set in motion a plan to pay off the entire debt by 2013. When George W. Bush took office he reversed the income taxes on America's rich and has since doubled the National Debt with record budget deficits, embracing a policy of "spend now, let someone else pay later".
CORPORATE CORRUPTION & CRIMEEnron, Worldcom and similar corporate scandals have shaken investor confidence in the United States and amongst foreign investors. U.S.-based energy trading firm Enron reported earnings of more than $100 billion in 2000. So when Enron collapsed a year later the financial community was stunned. Employees lost jobs and pensions. Some investors lost their entire life savings in what became the largest bankruptcy in American history. Top Enron officials were later found guilty of fraudulent accounting practices and of trying to hide hundreds of millions of dollars in debt. The telecommunications giant Worldcom was once considered among the most powerful in the world. But a 2002 investigation by the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission found company officials had inflated the value of the company's assets by $11 billion. Other scandals like Tyco International, Martha Stewart's insider trading, and Conrad Black's behind the scenes "non compete clause" hush money all made investors jittery about investing in companies with less than stellar reputations. The Investor Confidence Index measures the attitude of American/foreign investors to risk. In December 2003 the ICI was 109.0, but by December 2007 had dropped to 65.9 with all the corporate scandals in the news and the collapse of the housing market. If Investor Confidence continues to be poor the stock markets will continue to suffer turbulent times, and one way to increase investor confidence is for the US government to take corporate crime more seriously. Fiscal fraud doesn't just hurt the company in question, it hurts the whole industry.
HEALTH INSURANCE PROBLEMSAmerica is home to the western world's only privately run health insurance industry. Canada, South America, Central America and European countries all have free health care, and significantly cheaper health costs. The American health industry operates on the idea of profits first, health care second. The result is that when a patient needs medical treatment the hospitals first check to see if a person has health insurance that will cover the treatment, and if they don't they refuse to provide treatment. Within the health insurance industry there is a second problem, as health insurance companies refuse to pay for "pre-existing conditions", "non-life threatening illnesses", too fat, too thin, etc. resulting in many Americans having to pay for their health expenses out of their own pocket, or going in debt to pay for it. When people can't pay for their health care their work productivity suffers. America is becoming a nation of health care rejects, people who can't get health insurance or health care, and its creating a culture of invalids. America's obesity problem isn't helping either as its creating a working class that can't do heavy lifting, and in some cases are so morbidly obese they can't work at all. World Health Organization ranks the different health organizations around the world in terms of quality of service and America's ranks as 37, just 2 above Cuba (which has free health care), and no where near countries like France (1), Italy (2), Spain (7), Austria (9), Japan (10), Britain (18) and Canada (30). America needs two things in order to catch up with the rest of western world: Free health care and more funding to school physical education programs, which have been cut significantly in recent years. The problem in the USA is that free socialized health care is considered to be a "communist" idea, despite the fact the USA also has socialized police, firefighters, education, welfare, court systems and postal services.
HIGH OIL PRICESOn September 11th 2001 oil prices were $25/barrel. Since then oil prices have skyrocketed during two wars in the Middle East and supply concerns. On July 11th 2008 the price of oil reached a record $147.27 US/barrel. This kind of unprecedented price increase was previously unthought of and is largely the result of market speculation and increased demand from China, India and other growing markets. The problem with high oil prices is that it dramatically raises the price of agriculture and transportation, thus effecting all major industries. The US economy is dependent on oil for transportation and the economy would collapse if the oil well simply ran dry. The solution being pushed by politicians and environmentalists is the use of hybrid cars and eventually switching to hydrogen cars (still years away from mass production).
INFLATION & INTEREST RATESConsumer prices in the United States are skyrocketing at twice the expected rate, pushing up U.S. inflation to the highest level in 17 years due to the high cost of fuel, food and clothing. The inflation surge presents a major problem for the Federal Reserve: Will inflation force it to start raising interest rates even as the economy struggles to avoid a recession? If Federal Reserve doesn't raise interest rates it creates an economic imbalance (interest rates effect commodity prices, bonds, stocks and currency exchange rates) which would destabilize the American economy's investment system and many economists are worried about how it would effect foreign investors pulling out of an unprofitable United States. INTER-STATE MIGRATIONAmericans as a people have begun to migrate quite a bit in the last decade. Since 2000 cities like Detroit, Cleveland and Buffalo have seen hundreds of thousands of people migrate to cities like Las Vegas, Phoenix and Austin. Ohio for example is becoming a state of ghost towns and ghost cities. Four of America's fastest dying cities are in Ohio: Youngstown, Canton, Dayton and Cleveland. Other states & cities are seeing a huge population growth as people from small towns and cities all across America migrate to where they can find work. Evidently Americans are becoming more transient in their effort to find work, although no where near as bad as the Great Depression when whole populations of people moved from place to place trying to find work.
MORTGAGES & THE SUB-PRIME CREDIT CRISISThe problem of the sub-prime credit crisis essentially began when banks and financial institutions told home buyers to go ahead and buy homes they couldn't afford, just because interest rates were low. Thanks to that lack of wisdom the United States is now in the most severe housing crisis since the Great Depression, triggering the worst global credit crisis in a generation. The financial and banking industry has taken huge losses from the credit crisis, the result of giving mortgages on houses not really worth the stated amount. People were bidding on houses with money they didn't have, getting mortgages that they couldn't pay and when they defaulted on the loan (or the banks denied them re-financing because the house's value dropped) the bank ends up with a house not worth the amount they paid for it. Therefore the bank ends up selling the home at a huge loss. This isn't just limited to houses however. Businesses and car manufacturers are also being affected. Automakers are having difficulties securing credit to finance auto leases, builders have a 10-month supply of unsold new buildings, and prices for existing buildings fall month after month. It is essentially a housing and credit crash. The worse the economy gets, the more people need cheaper homes... so the prices drop and the banks lose more money, causing a cyclical plummet in the prices. In the summer of 2007 the American housing market was worth a collective $20 trillion US, but has since lost an estimated $8 trillion in residential real estate value and prompted over $500 billion in writeoffs at the world's largest banks and brokerages. How many more financial giants will fail due to US junk mortgages? Britain's Northern Rock PLC, the biggest UK mortgage lender, New York-based Bear Stearns Cos., the fifth-largest U.S. investment bank, the world's largest bank Citigroup Inc. and the world's biggest brokerage, Merrill Lynch Inc., Wachovia Corp., the US "super-regional" bank have all suffered huge losses which are being bailed out by other mortgage houses, banks and the US government. Even the financial institutions don't know the full extent of what is in their books and how many losses they can expect to wrack up. They have been propagating the myth that the "worse is over", but instead are announcing bigger and bigger losses. As such the CEOs of financial institutions are rapidly losing credibility as its evident they don't know the full extent of the problem. You might ask where did all the money go? The Americans who sold their homes just prior to the mortgage credit crisis are the ones who are lucky. They've gotten away Scot-free with almost double the current value of their old homes.
Its not just banks that are dealing in too much credit. Americans in general have too much private debt from car loans, credit cards, university loans, and mortgages. According to a 2007 report the average American (including children) owes $143,362 in combined credit card, loans and mortgage debt. Its reached a point where the American dollar doesn't really seem worth the paper its printed on when American's are using plastic more than they actually make. And if American's can't afford to pay their debts it really is no surprise the biggest source of debts, mortgages, was the first to cause a credit crisis. WEAK AMERICAN DOLLARThe growing economies of Europe and Asia has resulted in currencies that are growing in popularity. In the past economic stability in the US has resulted in a strong American dollar, but since 2001 this economic stability has been non-existent. Battered by September 11th, Enron, Worldcom, two wars in Afghanistan and Iraq and a host of other problems the US economy is now quite unstable. Thus currencies which are stable, like the Euro, have been growing in popularity as banks stockpile the most reliable/desirable currencies. Global banks thus have been cashing in American dollars (thus lowering the demand for the US buck) in favour of Euros. The demand for Euros has resulted in the currency's more recent strength. The problem with a weak American dollar is that it creates a lot of problems for imports and exports as the dollar fluctuates more rapidly and international business contracts dealing in US currency are therefore effected if the value goes up or down suddenly. In recent years some international companies have taken to dealing with Euros instead of dollars, finding it to be a more stable currency. The American dollar will continue to be weak and battered as long as the American economy and government is unstable.
BARACK OBAMAWhen Barack Obama was elected in Autumn 2008 and was sworn in as the new President of the United States in January 2009, many Americans thought an era of change was upon them. And while some things have changed since then, change is ALWAYS a slow process. Obama's campaign mantra HOPE was the real focus, but many Americans hope for different things like the economy to improve, better environmental practices, and free medicare for everyone. One of the first things Obama did once in power was to realocate enough money to provide free basic medical care to all Americans. It was a start and he did it without raising any taxes. What he did instead was reduce the amount of money that rich people get back on their income taxes if they made charitable donations. That reduction + the realocation of money from a Bush-era program for seniors health care was enough to provide the magic number needed to give free basic medical care to all Americans. The problem however is that it didn't stop there. "Basic" quite literally means very basic. Obama's goal since then has been to expand on that program and try to get more things covered, to adopt a healthcare platform similar to Canada, Europe and other countries which have much better than health care systems than the USA does (the USA ranks so low it is below Cuba and very few politicians in the USA has been willing to fight for universal healthcare). Another thing Obama did was refocus America's attention on Afghanistan and finding Osama bin Laden. This refocusing of energies led to the death of Osama bin Laden on May 2nd 2011 when a team of Navy Seals stormed bin Laden's compound in Pakistan and the terrorist leader went down fighting. The most important thing Obama did however was to stimulate the American economy by pumping cash into building public works like new roads, highways, hospitals, schools, etc. The goal was to get America working again so the economy would pick up. Which it did, but the progress has been slow. Eventually the economy recovered and strengthened.
CURRENCY WAR WITH CHINAOne of the biggest problems with America's economy is the shortage of manufacturing work available. Many factories have been moved overseas to China and the USA's economy is now floundering because of it. China's currency, the Yuan, is deliberately deflated and pegged to the US dollar by the Chinese government. They rarely allow the currency to go up in value. Right now the Chinese Yuan is worth about half or one-third of what it really should be worth. Thus products from China cost 50% to 66% cheaper just because of the currency adjustment, and not because their workers work for a lot less than Americans do. It is an unfair practice and even the World Trade Organization has agreed with this and has been pressuring China to allow their currency to float on the open market. But China outright rejects pressure to allow its currency to float. Which leaves the USA with several options: #1. Add tarriffs (import taxes) to Chinese products coming into the USA, which the US government (regardless of who is in the White House) probably won't do because the USA owes China a lot of money for the national debt. #2. Deflate America's currency by printing more American money. This is something Obama is already doing. In November 2010 the U.S. Federal Reserve announced plans to expand the basic money supply by $600 billion USD by June 2011. #3. Peg the US dollar to the Yuan, but at a higher rate. If China can peg the Yuan to the dollar, why can't the USA do the same? Really what it comes down to is that the USA is now in a currency war with China, but they haven't come to a solution yet. See Also: The Enslavement of the American People
If you want to learn about the United States we recommend the following websites: cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/ The CIA World Factbook is a wealth of information on various countries in the world, everything from population, technology, military numbers and so forth. Lots of technical data there is very useful if you are researching the USA or any other country. Federal Publications Seminars provides updates on a variety of areas of interest including federal regulations, federal grants, government contracting, international arms trafficking regulations, legal education, training programs, books, events, webinars. The only thing better than learning about the USA online is actually visiting the country and learning first hand what the country is like. The United States is a fantastic place and well worth exploring if you have a streak of wanderlust.
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Website Design + SEO by designSEO.ca ~ Owned + Edited by Suzanne MacNevin | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||